Search Knowledge Base by Keyword
What Is Horizontal Scaling And How It Works
In this guide, we will explore what horizontal scaling is, how it functions, and how to adjust the limits of your cloud environment effectively.
With the UKHost4u Cloud Solutions Platform, you can automatically scale any web application and website both vertically and horizontally. This ensures that as your web applications gain popularity and traffic increases, your resources expand accordingly.
In this article, we will cover how to set up your environment’s horizontal scaling, both manually and automatically. Below is a quick outline to help you navigate through the content:
- Horizontal Scaling
- Horizontal Scaling Modes
- Horizontal Scaling Specifics
- Managing Horizontal Scaling Nodes Within Layers
- Automatic Horizontal Scaling
- Triggers for Automatic Horizontal Scaling
- Automatic Horizontal Scaling Execution History
By the end of this guide, you will have a clear understanding of how to manage and optimize horizontal scaling for your web applications.
Horizontal Scaling: Multi Nodes
To manually scale your environment horizontally, follow these steps:
- Open your environment topology wizard.
- For each node, use the “+” and “-” buttons or the slider to adjust the number of nodes according to your requirements.
This simple process allows you to efficiently manage your resources and ensure your environment can handle increased demand.
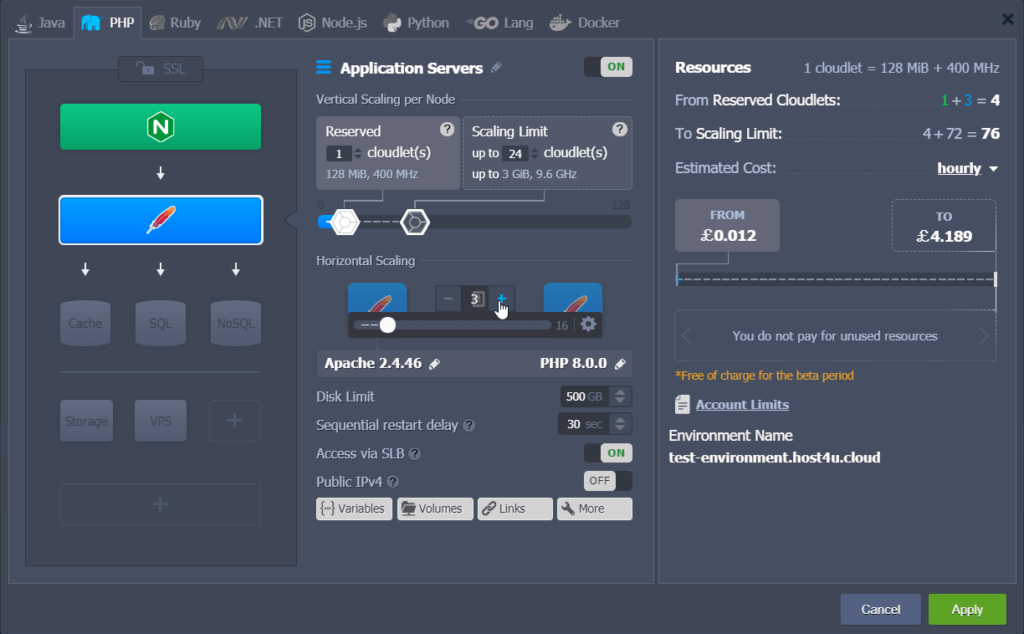
PLEASE NOTE:
- Automate Horizontal Scaling: Check this section to learn how to automate horizontal scaling based on incoming load using tunable triggers.
- Storage Server: You can use the master (initial) node of the layer as your storage server to share data across the entire layer.
- Scaling Down: When decreasing the number of nodes, the last container added to the layer will be the first to be removed unless you select one explicitly.
- Choosing Scaling Mode: Select the required scaling mode from the drop-down list. Refer to the “Horizontal Scaling Specifics” section for more details.
Scaling Modes
When creating or editing your environment, you can select your preferred scaling mode:
- Stateless: Simultaneously creates all new nodes from the base image template.
- Stateful: Sequentially copies the file system of the master container into the new nodes.
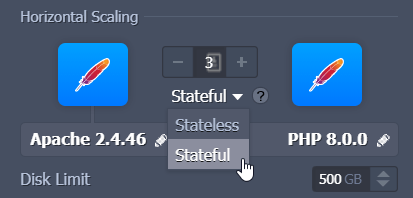
When selecting the stateless mode, it is generally faster, while the stateful mode automatically copies all custom configurations.
Even in stateful mode (if no customizations have been applied yet), all nodes are created simultaneously, speeding up the initial layer creation process.
However, with the stateless mode, be aware that the following features will be missing on the new nodes within the layer:
- Deployments: Existing project contexts won’t be transferred.
- Custom SSL: SSL certificates and configurations won’t be copied.
- Mount Points: Custom mount points will only be moved if the appropriate volume is configured.
- Add-ons: Any add-ons installed on the layer won’t be available.
PLEASE NOTE: Custom file transfers with the stateless mode can be done manually or configured via Cloud Scripting automation.
Given this, we recommend the stateful mode for the load balancer, application server, and VPS stacks. However, you can always manually adjust and redefine the scaling mode for your nodes using your environment’s topology wizard.
What are the Horizontal Scaling Specifics?
The limit for the same-type server within the same environment layer is set to 16 nodes. All newly added servers are created on different hardware nodes, providing advanced reliability and high availability.
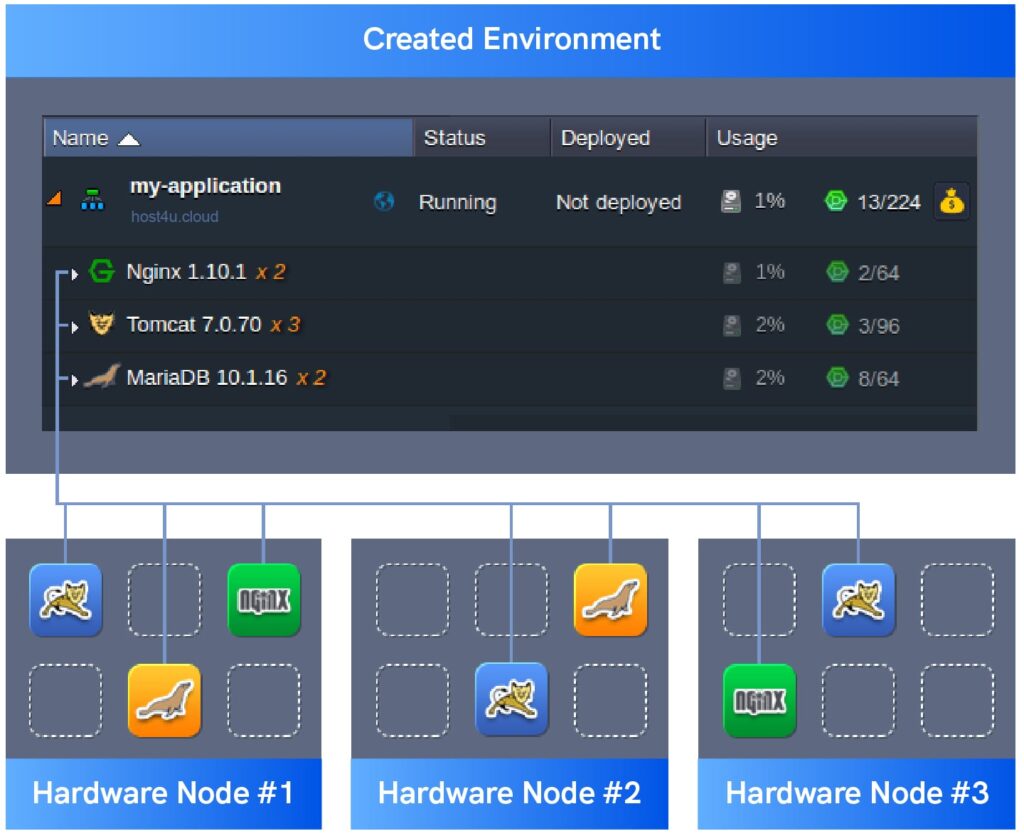
Each environment node group or layer is assigned a dedicated name. If necessary, you can manually edit your environment’s layer names. When adding multiple instances within your environment, the layer name will be complemented with the xN label (where N corresponds to the actual node number).
Having multiple same-type nodes within a layer enables synchronous management. This allows you to:
- Simultaneously configure all containers
- Inspect logs and statistics for all containers
- Restart or redeploy all containers through the corresponding icons
This synchronous management streamlines the process and ensures consistency across your environment.
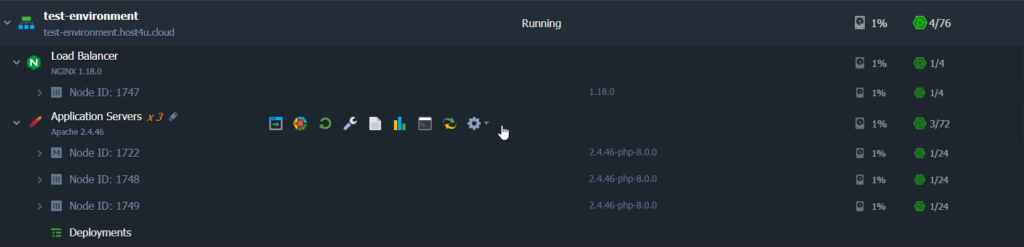
To operate with a particular container separately, click on the container to see the full list of its nodes and expand the layer’s string.
Each of these containers is an isolated instance with a unique Node ID, allowing for individual access and configuration. You can easily identify the Master Node by its dedicated icon, marked as “M”.
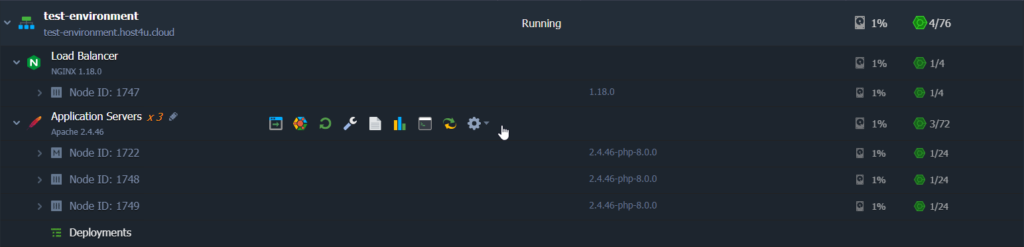
To facilitate interactions between several servers of the same type, the UKHost4u Cloud Platform allows you to label specific nodes to define either the master or slave instances within a DB cluster.
To change a node’s label:
- Expand the container selection.
- Double-click on the default Node ID (xxx) or hover over the pencil icon.
- Specify the new node’s name.
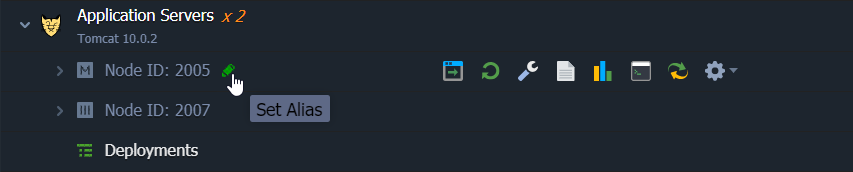
Feel free to check our Environment Aliases article for more information.
PLEASE NOTE: If you are scaling different types of stacks, consider the following specifics:
- Application Server Instance: When scaling, the load balancer node will be automatically added to the environment topology.
- High-Availability Feature: If enabled for your application server, the required NGINX load balancer cannot be scaled horizontally. If multiple NGINX nodes were available before, they will be automatically downscaled to a single instance.
- VPS Nodes: Each VPS node is provided with a separate public IP address.
- Maven Nodes: Maven is the only node that can’t be scaled horizontally.
Now, you know how horizontal scaling works and how easy it is to horizontally scale instances with the UKHost4u Cloud Solutions platform. Next, let’s see how to configure automatic node scaling and handle high load spikes without paying for limits you’ll never reach.
How to Manage Nodes Within a Layer
The UKHost4u Cloud Platform provides an easy and intuitive node management system. You can specify the required number of containers in a layer.
PLEASE NOTE: When you remove a container, the most recent containers are removed first.
How to Delete a Specific Node
If you need to delete a specific node, you can either:
- Access the Horizontal Scaling section in your environment topology wizard.
- Click on the “Change Environment Topology” button for the required environment.
- Click on the “+” or “-” button to make your changes.
- Click on the bin icon to delete a specific node.
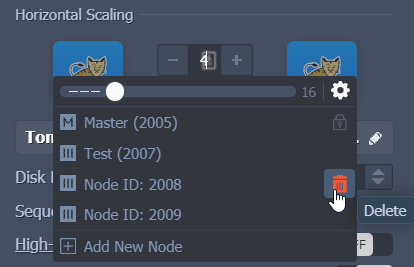
- Delete the node using the dedicated Scaling Nodes option in the dashboard.
- Expand the container.
- Hover over the scaling node and click on the Additionally button.
- Click on the Delete button of the particular node.
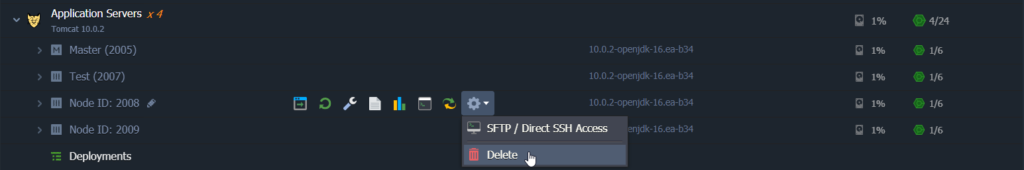
How to add or remove a node
Open the Scaling Nodes window in your environment topology wizard and:
Click on the”+” or Add New Node buttons.
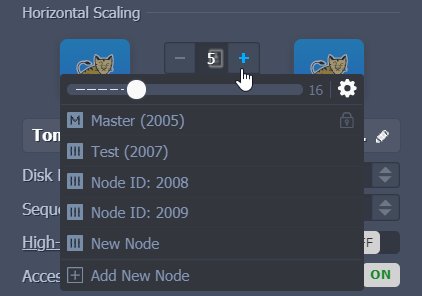
PLEASE NOTE:
- If the high availability feature is enabled for the layer (for Tomcat and TomEE application servers only), the nodes will be added and removed in pairs.
- Empty containers represents stateless mode nodes and filled one for stateful.
Click on the “-” or the “bin” icon (when hovering over the particular node) to remove instances.
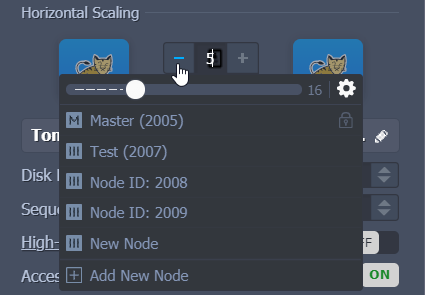
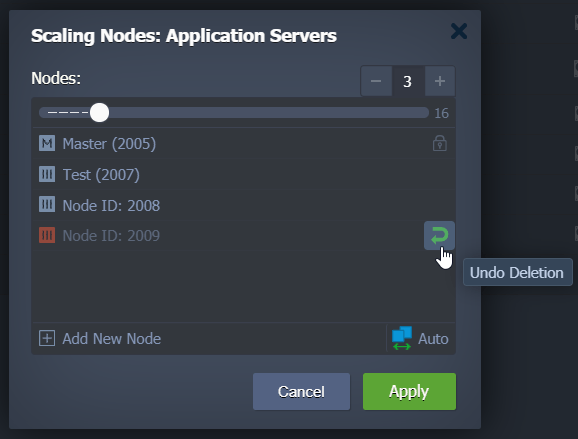
If you want to undo the node’s removal:
- Open the Node’s settings.
- Click on the Additionally button.
- Click Delete.
- Finally click on Undo Deletion.
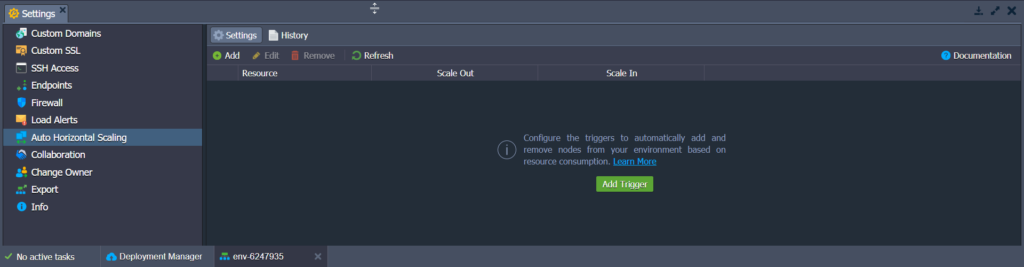
3. You will find the Automatic Horizontal Scaling section in your environment’s settings.
4. When you apply changes, our UKHost4u Cloud Platform will automatically notify you about all the potentially harmful actions (if any) that will be performed with your environment such as:
- Nodes restart notifications.
- Layers and separate nodes removal reminder.
- Impact on existing NFS mounts.
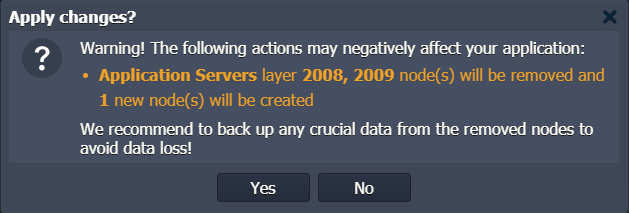
Before proceeding, safely back up your data to ensure that the listed points won’t affect your application, or any crucial data (from the removed nodes).
Automatic Horizontal Scaling
As mentioned earlier, in addition to the inbuilt automatic vertical scaling, UKHost4u Cloud Platform can automatically scale nodes horizontally. This changes the amount of containers within a layer to efficiently distribute the incoming traffic.
This means that load between all instances within the same layer are evenly distributed. To ensure reliability and high-availability of the hosted projects, a new container is created and placed at the host with the least number of instances from the same layer to the lowest load mark.

Automatic horizontal scaling is implemented with the help of “triggers”, which are, in short, custom conditions for node addition (scaling out) and node removal (scaling in) based on the present load.
To decide if the node count adjustment is required, every minute our cloud platform analyses the average consumption of the resources (the number of minutes is specified within the trigger).
PLEASE NOTE: The statistic is gathered for the whole layer. For example, if there are 3 nodes, which are loaded for 20%, 60%, and 25% respectively, then the calculated average value is 35%.
Furthermore, the scale in and out conditions are completely independent to each others. As such, the analyzed period for one is not reset when another one is executed.
Triggers for Automatic Scaling
PLEASE NOTE: When a single certified application server (except a custom Docker container) is scaled out on an environment without load balancers, the NGINX balancer will be deployed automatically. However, if you need a different load balancer for your application, then you should add it manually before scaling event.
To configure a trigger for the automatic horizontal scaling:
1. Click on the Settings button for the required environment.
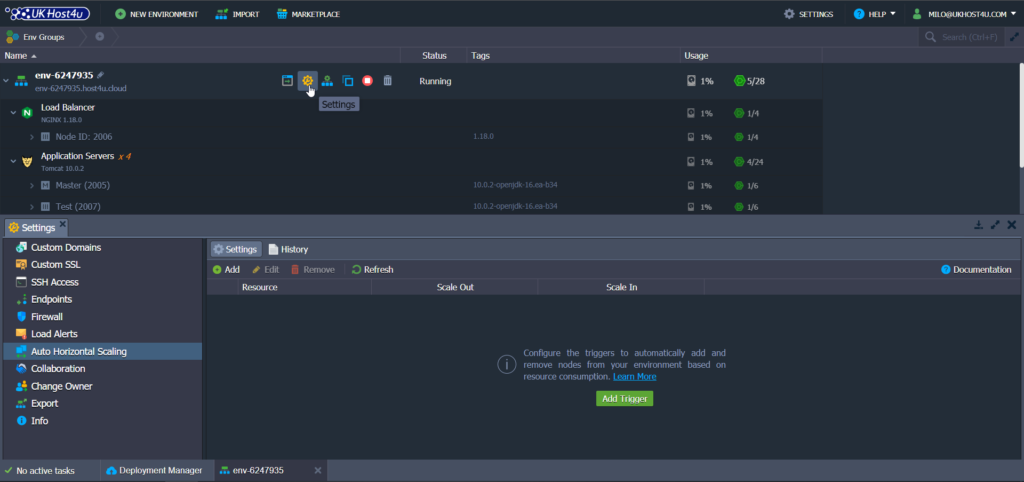
2. In the opened tab, navigate to the Auto Horizontal Scaling section (see above).
You can manage auto horizontal scaling for the environment with the following features:
- Add: to create a new trigger.
- Edit: to adjust the existing trigger.
- Remove: to delete unrequired trigger.
- Refresh: to update the displayed list of scaling triggers.
Click Add to proceed.
3. Select the required environment layer from the drop-down list and choose the resource type to monitor via one of the appropriate tabs: CPU, Memory, Network, Disk I/O, Disk IOPS.
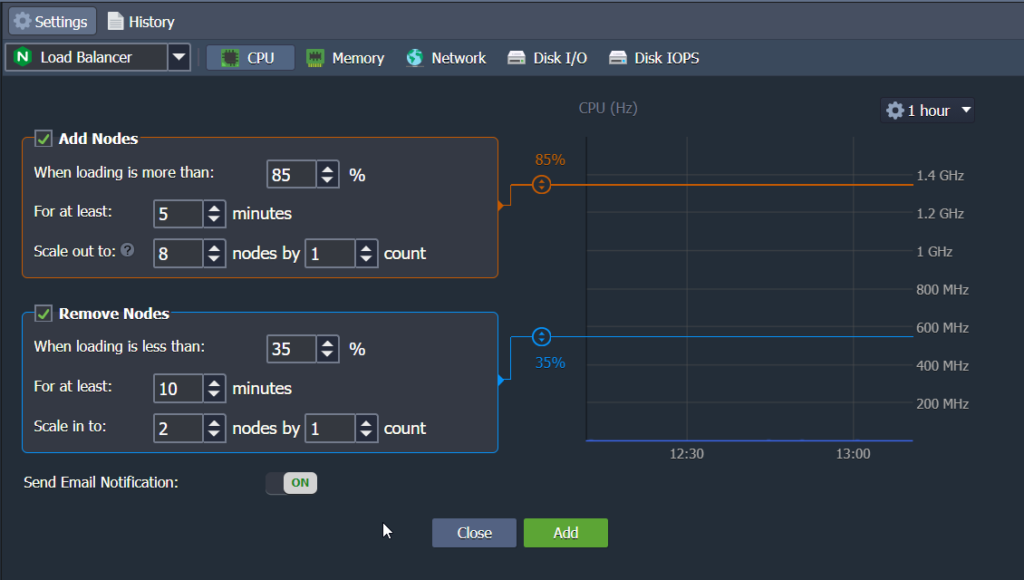
Our advice:
- You can use the Master node as a storage server. For example, you can share data within the whole layer, including nodes added through automatic horizontal scaling. The CPU and Memory limits are calculated based on the amount of the allocated cloudlets.
4. On the image below you can see how to visualise the consumption usage over a particular period of time. Simply, using the drop-down list, select the required period you want to display your data. You can also enable/disable the statistics’ Auto Refresh function from there.
5. For each trigger, you can “Add” and “Remove” nodes conditions. You can also enable it with the corresponding check-boxes.
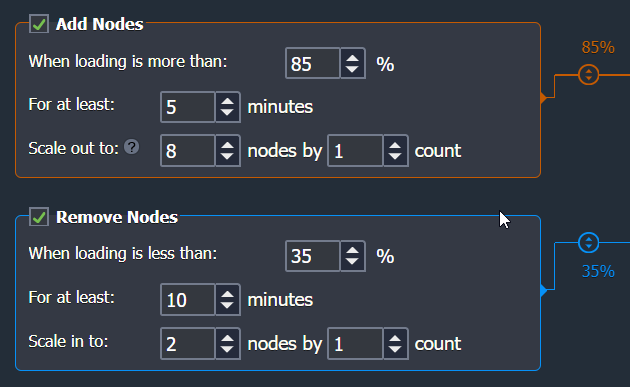
Now, let’s go through an example where both are configured the same way:
- When loading is more than the upper limit in percentage for the average load ( it executes the trigger if exceeded).
- When loading is less than the lower limit in percentage for the average load (it executes the trigger if exceeded).
PLEASE NOTE:
- Values can be stated using the sliders on the graph.
- The 100% value automatically disables the Add Nodes trigger, and 0% the Remove Nodes one.
- 20% is the minimum difference allowed between Add and Remove Nodes conditions.
- Mbps units can be selected for the Network trigger instead of the percentage.
- We recommend setting the average loading for the Add Nodes trigger above the 50% threshold to avoid unnecessary scaling such as wasted resources or funds.
- For at least: corresponds to the number of minutes the average consumption is calculated for (up to one hour with a 5 minutes step, such as . 1, 5, 10, 15, etc.).
- Scale out (in) to: is the maximum or minimum amount of nodes for the layer, that can be configured due to automatic horizontal scaling.
- Scale by: is the count of nodes that are to be added/removed at a time upon trigger’s execution
When you configure a trigger, keep in mind the layer’s scaling mode. For instance, you should set lower loading percent in the “Add Nodes” trigger for a stateful mode, as content cloning requires some time and you can reach resources limit before a new node is created.
6. Using the toggle button you can also set up automatic email notifications. If you don’t want to receive updates, simply select the “OFF” option.

7. At the bottom of the page you will find the following buttons:
- Undo Changes: which brings you back to the previous state (in editing mode only).
- Close: it exits the dialog without changes.
- Apply or Add: applies or confirms changes for the trigger.
Select the required option to finish the trigger creation or its adjustment.
How to trigger the execution history
If you need to check your scaling triggers’ history for a particular environment:
- Open up your environment’s Settings.
- Select Auto Horizontal Scaling option.
- Click on the History button to display the triggers execution history.
PLEASE NOTE: You can additionally customize the period to display triggers activity using the From and To fields.
When a trigger has been executed, you will be able to see in details its:
- Date and Time of the trigger execution.
- Action performed (Add or Remove Nodes).
- Nodes type the scaling was applied to.
- Info about the trigger execution condition.
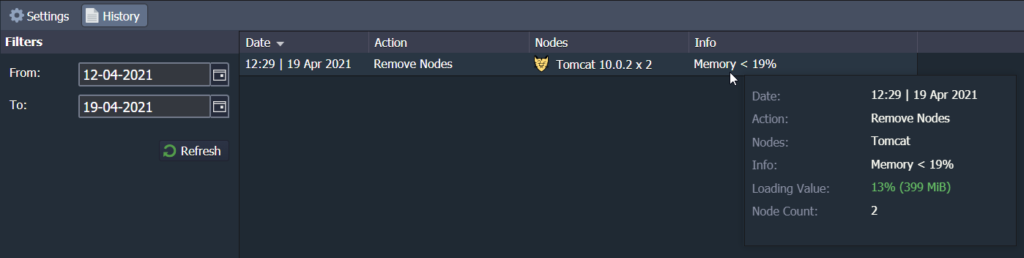
If you need extra details, hover over the particular record to check the Loading Value which will display the resource usage on the moment of execution and Node Count resulting number of nodes.
PLEASE NOTE: The Add and Remove Nodes triggers are independent to each other. If the removal condition average load is not reset then it continues to check even after a new node addition. This approach provides a quicker detection of the sufficient average load during a specified interval.
We recommend you to set a significant difference between scaling out and scaling in limits to avoid too many topology changes.
That’s it! Now you know all about manual and automatic horizontal scaling, how to configure a set of tunable triggers to ensure your application performance and track automatic horizontal scaling activity directly via the dashboard.
If you have any questions or need further assistance with your horizontal scaling, feel free to contact our 24/7 support team!
Next Steps:
- Vertical Scaling
- Import an environment
- Create an environments’ group
